This example demonstrates the two different execution semantics of composite states: child-first and parent-first execution.
Child-first vs. Parent-first Execution
Event Buffering
This example demonstrates the usage of event buffers and their impact on the event processing of a state machine.
Event-driven vs. Cycle-based Execution
This example demonstrates the two different execution semantics of statecharts: event-driven and cycle-based execution.
Hierarchical Statecharts
This example demonstrates the usage of hierarchies in statecharts. It explains the concepts of composite states and subdiagrams.
History States
This example demonstrates the usage of history states and explains the difference between a shallow and a deep history.
Multi State Machines
This example demonstrates the usage of multi state machines.
Orthogonal States
This example demonstrates the usage of orthogonal states as well as of forking and joining synchronization nodes.
Superstep Semantic
This example demonstrates the usage of superstep semantic and its impact on the state machine execution.
Basic Tutorial
This is a series of examples demonstrating multiple features of CREATE SCT. With each iteration, more features are shown. This example is a good starting point to dive into SCT headfirst.
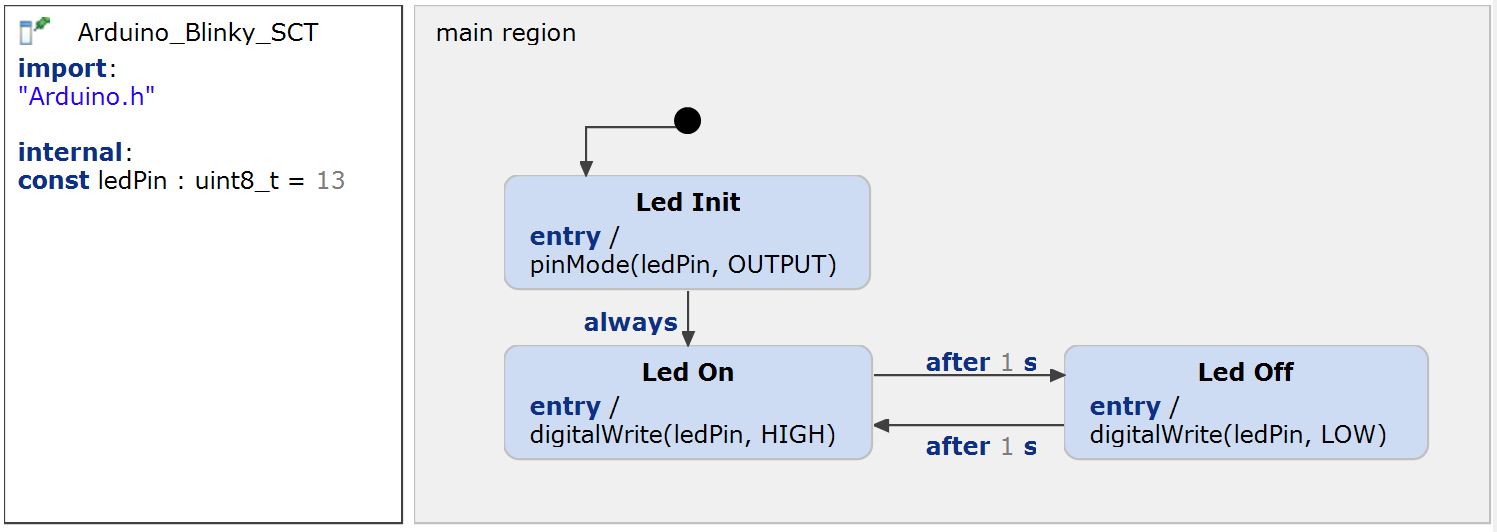
Arduino - Blinky LED (Deep C++)
This is a simple example of how to use the C/C++ Domain together with an Arduino. C++ Timer are integrated
C Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate C code from a statechart.
C++ Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate C++ code from a statechart.
Java Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate Java code from a statechart.
C Code Generation for Multi State Machines
This example demonstrates how to generate C code from a multi state machine scenario.
C++ Code Generation for Multi State Machines
This example demonstrates how to generate C++ code from a multi state machine scenario.
Java Code Generation for Multi State Machines
This example demonstrates how to generate Java code from a multi state machine scenario.
Python Code Generation for Multi State Machines
This example demonstrates how to generate Python code from a multi state machine scenario.
Python Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate Python code from a statechart.
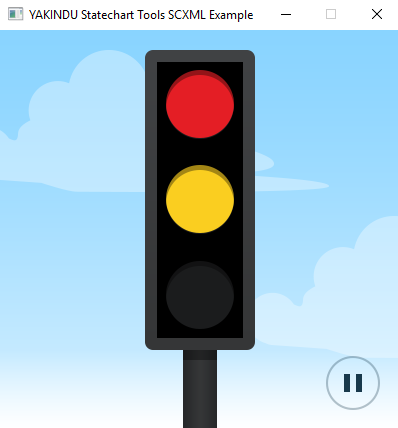
SCXML Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate SCXML code from a statechart.
Coffee Machine (Deep C)
This is a comprehensive example for the deep integration of CREATE statecharts with manually written C code. The example is implemented as a simple command line tool.
Coffee Machine (Deep C++)
This is a comprehensive example for the deep C++ integration of CREATE statecharts.
Arduino - Digital Watch (C++)
This digital watch was first designed by David Harel, the founder of the Statecharts Theory. This example shows how to integrate it on an Arduino.
Digital Watch
This digital watch was first designed by David Harel, the founder of the Statecharts Theory. He described it in "On Visual Formalisms", published in "Communications of the ACM" in May 1988. A digital watch by that time had a display to show just a few digits. Using four control buttons, the user was able to toggle between displaying the time, displaying the date, using a stopwatch, maintaining an alarm, and setting time, date, and alarm.
Elevator with SCTUnit
This video tutorial is presented by Prof. Tom Mens (Software Engineering Lab, University of Mons). It provides a hands-on demonstration, on the basis of a simulation of an elevator statechart, on how to write and run unit tests for statecharts with Itemis CREATE.
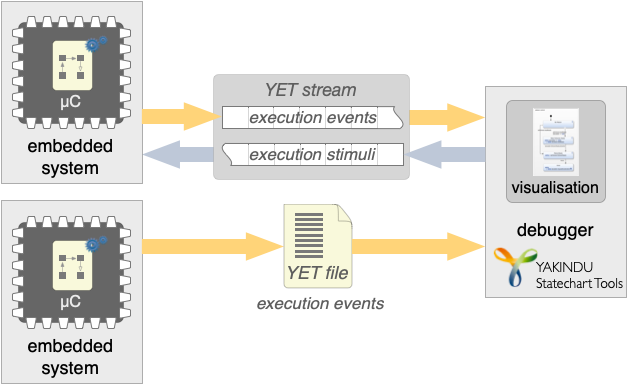
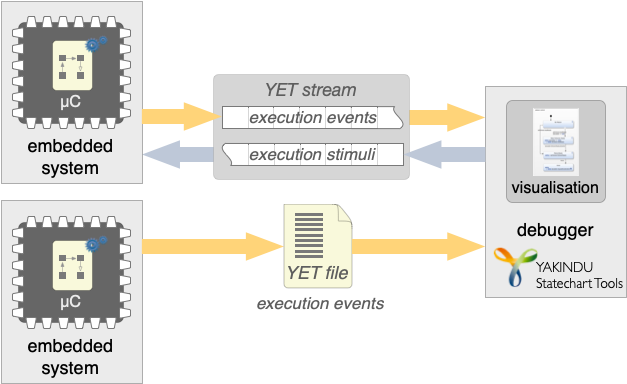
ESP32 - Tracing & Remote Control (C)
CREATE provides infrastructure for debugging and remote controlling the state machines using execution traces (YET).
FMU Code Generation
This example demonstrates how to generate an FMU from a statechart.
FreeRTOS C
This example is using the C Code Generation example and shows how to integrate FreeRTOS.
Arduino - HMI with LCD Keypad Shield (C++)
Expandable HMI example for Arduino using a 16x2 LCD Keypad Shield
Arduino - Bare-Metal Interrupts (C)
Embedded Systems Integration Guide - Arduino with @CycleBased or @EventDriven execution using Interrupts.
Arduino - Bare-Metal Polling (C)
Embedded Systems Integration Guide - Arduino with @CycleBased or @EventDriven execution using Polling.
FreeRTOS - RTOS Integration (C)
Embedded Systems Integration Guide - FreeRTOS Integration.
Zephyr - RTOS Integration (C)
Embedded Systems Integration Guide - Zephyr Integration.
Arduino - Basic Finite State Machine (C)
A very basic state machine example for the Arduino platform that switches an LED on and off. It demonstrates how to get started with Itemis CREATE and the Arduino platform and contains a timer service for the Arduino. You need to have an Arduino plugin, as described in the "Traffic Light Ported to Arduino" example.
MSP430 - Blinky LED (Deep C)
Blinking LED on MSP430G2553 by using TIs Code Composer Studio and Itemis CREATE as a plugin
Raspberry Pi - Hello World (C)
This example shows how to use a statechart and some C code to control a RGB LED attached to the Raspberry Pi.
C Code Generation for SCTUnit with GTest
This example demonstrates how to generate GTests for SCTUnit tests.
C++ Code Generation for SCTUnit with GTest
This example demonstrates how to generate GTests for SCTUnit tests.
Java Code Generation for SCTUnit with Mockito
This example demonstrates how to generate JUnit tests for SCTUnit tests.
Python Code Generation for SCTUnit with unittest
This example demonstrates how to generate unittests for SCTUnit tests.
Testing State Machines with SCTUnit
This example demonstrates how to write tests for statecharts using SCTUnit.
STM32F407 Discovery - Blinky LED (Deep C)
This is a simple example of how to use the C domain together with an STM32F407 Discovery board. C timers are integrated.
STM32F407 Discovery - Blinky LED (Deep C, Multi SM)
This is a simple example of how to use multi state machines in the C domain together with an STM32F407 Discovery board. C timers are integrated.
TicToc - Tracing & Remote Control (C)
CREATE provides infrastructure for debugging and remote controlling the state machines using execution traces (YET).
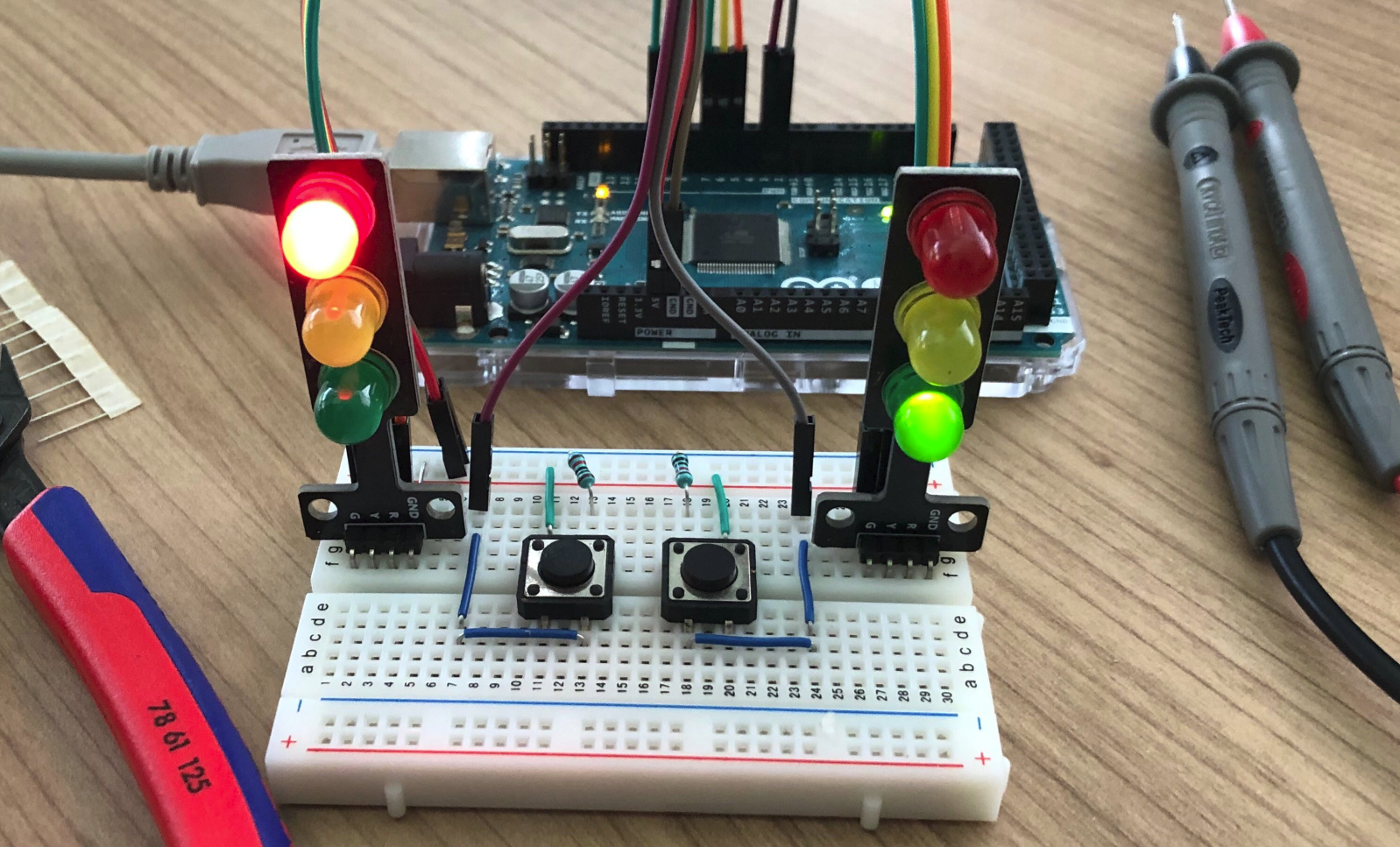
Arduino - Traffic Light (C)
Wondering how to execute your state machine on the Arduino platform? This example demonstrates the necessary steps, like installing the Arduino plugin, building the hardware, turning your statechart into code and uploading it to the Arduino. It does so by means of the standard traffic light example.
Arduino - Traffic Light (C++)
Wondering how to execute your state machine on the Arduino platform? This example demonstrates the necessary steps, like installing the Arduino plugin, building the hardware, turning your statechart into code and uploading it to the Arduino. It does so by means of the standard traffic light example.
Traffic Light (Qt/C++)
CREATE provides a Qt specific C++ code generator for statecharts. This example project shows how easy CREATE Qt/C++ state machines can be integrated into Qt applications.
Traffic Light (Java)
Demonstrates how to to generate Java source code from a statechart. The procedure is actually explained in the Itemis CREATE documentation, section "Java code generator".
Traffic Light with Multi State Machines
This example of the traffic light control demonstrates how to model multiple state machines that communicate with each other.
Raspberry Pi - Traffic Light (Python)
Demonstrates how to generate Python source code from a statechart.
Traffic Light (Python)
Demonstrates how to generate Python source code from a statechart.
Traffic Light (SCXML) for QT
This traffic light is inspired by the Qt examples. It provides a simple traffic light that consists of the main states red, yellow and green. It demonstrates how to connect to the active properties of a state in a dynamically loaded statemachine within Itemis CREATE and the Qt environment.
Zephyr C
This example is using the C Code Generation example and shows how to integrate Zephyr.
Arduino - Zowi (Deep C++)
This is a example of how to use the C/C++ Domain together with the Zowi by BQ. C++ Timer are integrated